-
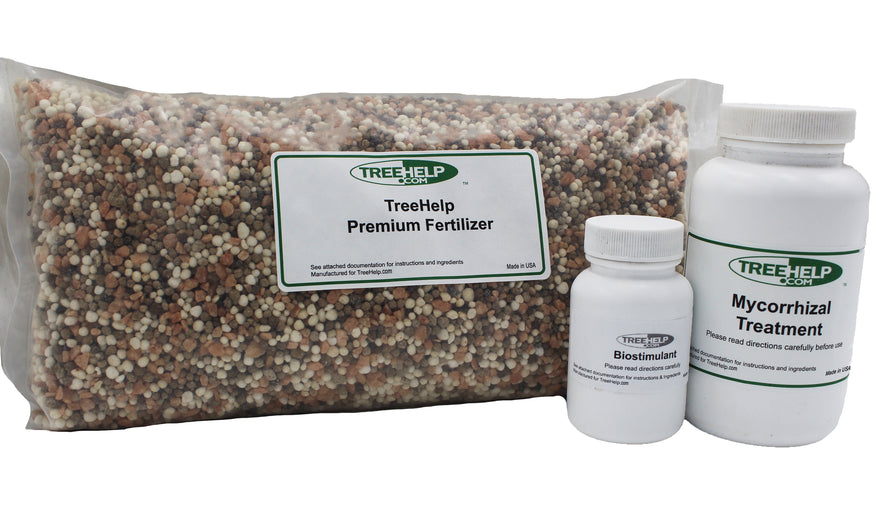
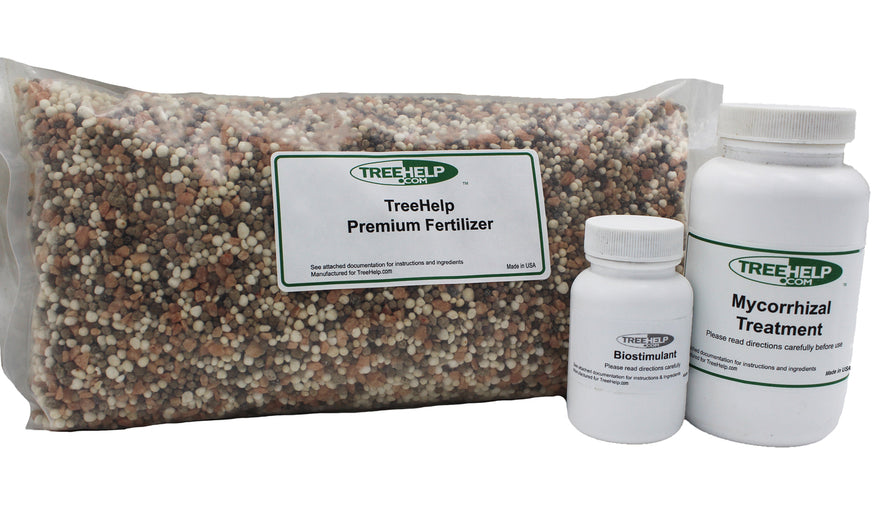
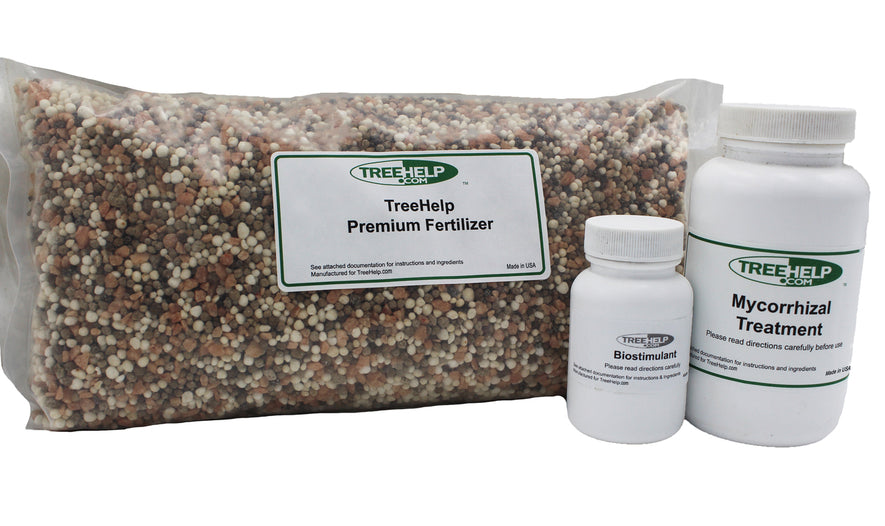
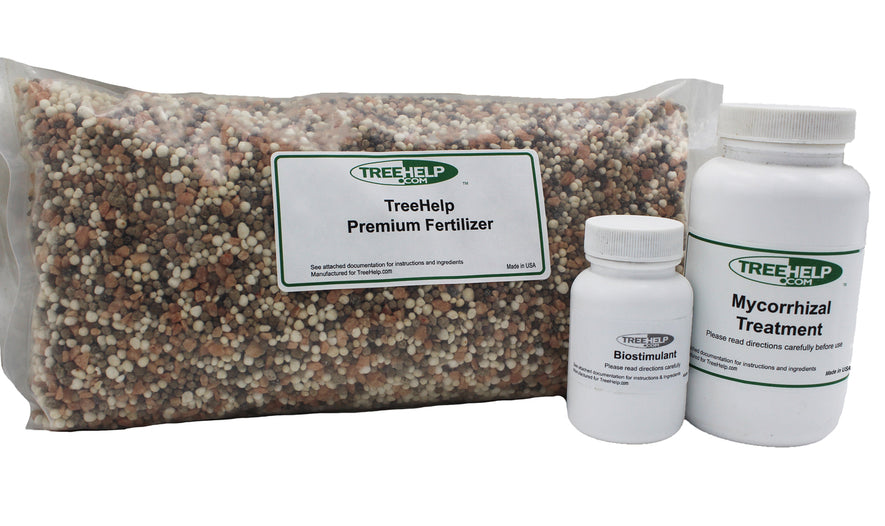
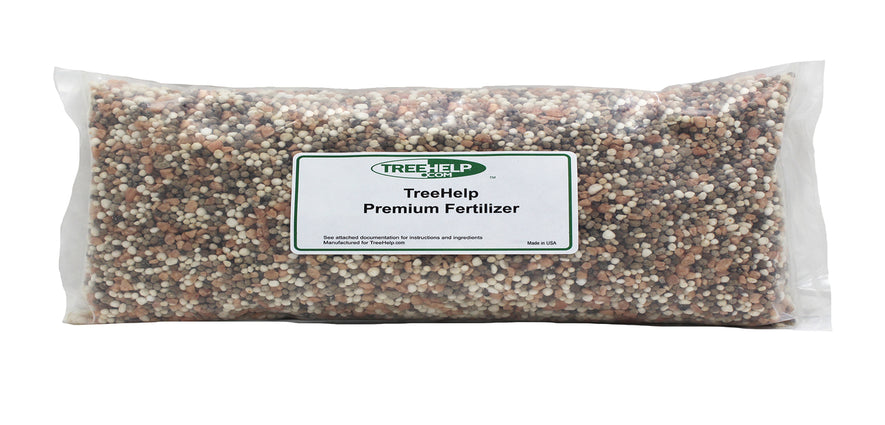
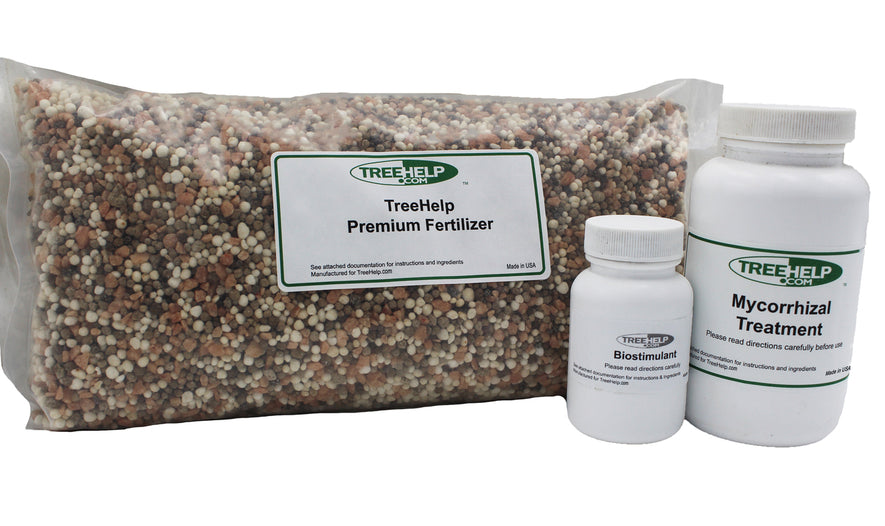
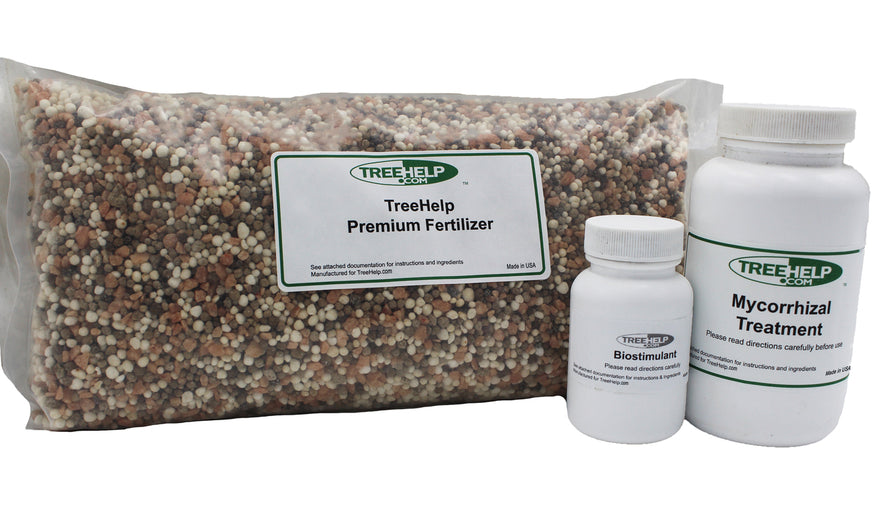
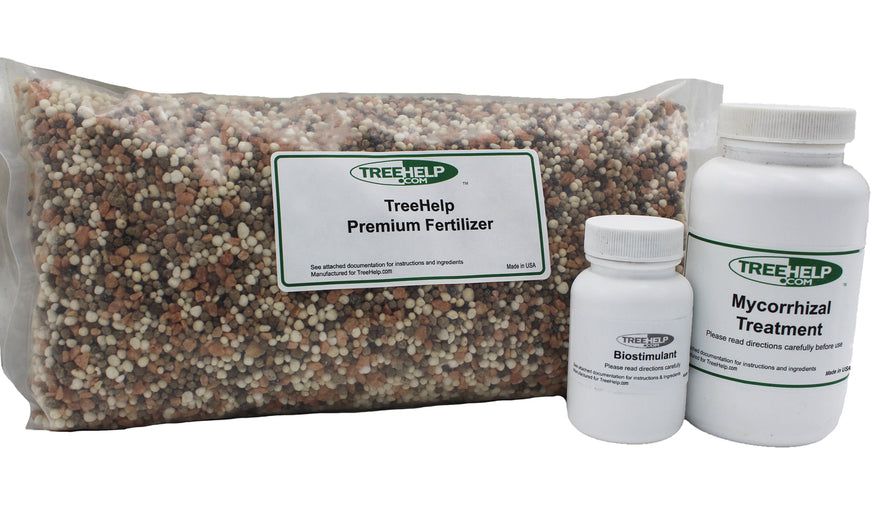
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits provide health...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
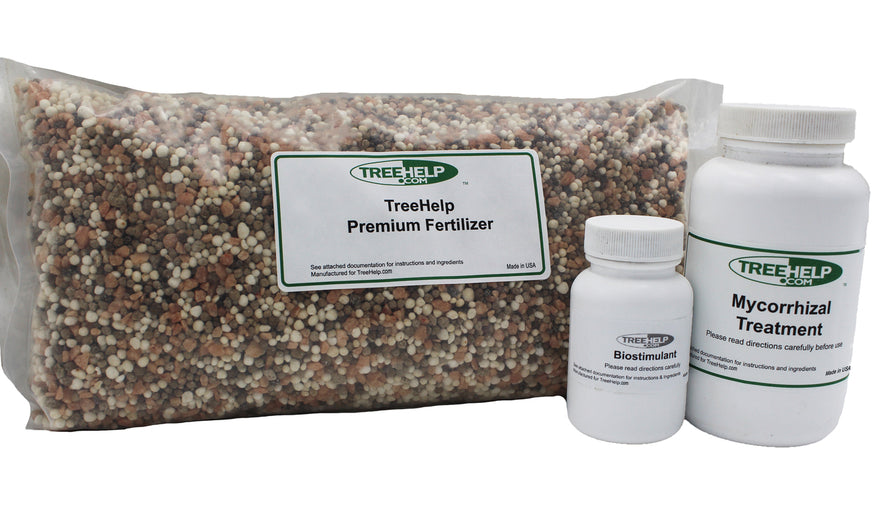
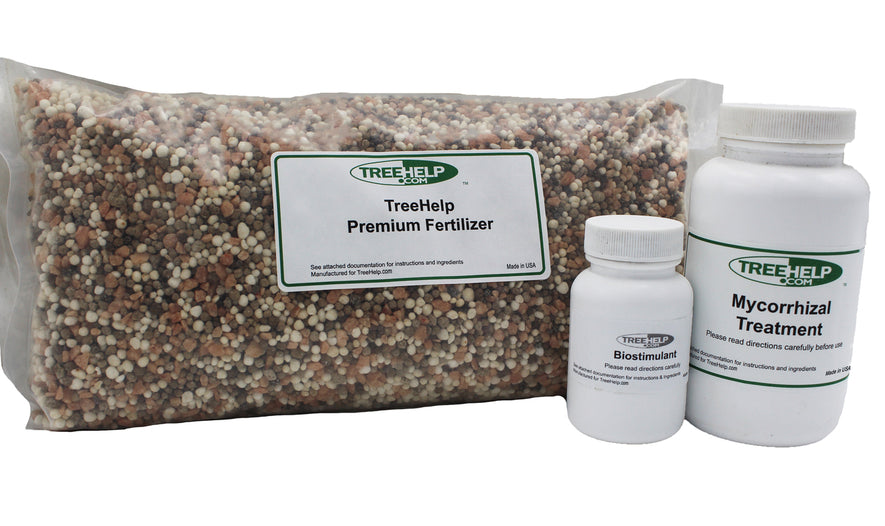
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Oak TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant oak trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits for...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Maple TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant maple trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits for...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Birch TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant birch trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits for...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Dogwood TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant dogwood trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits for...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
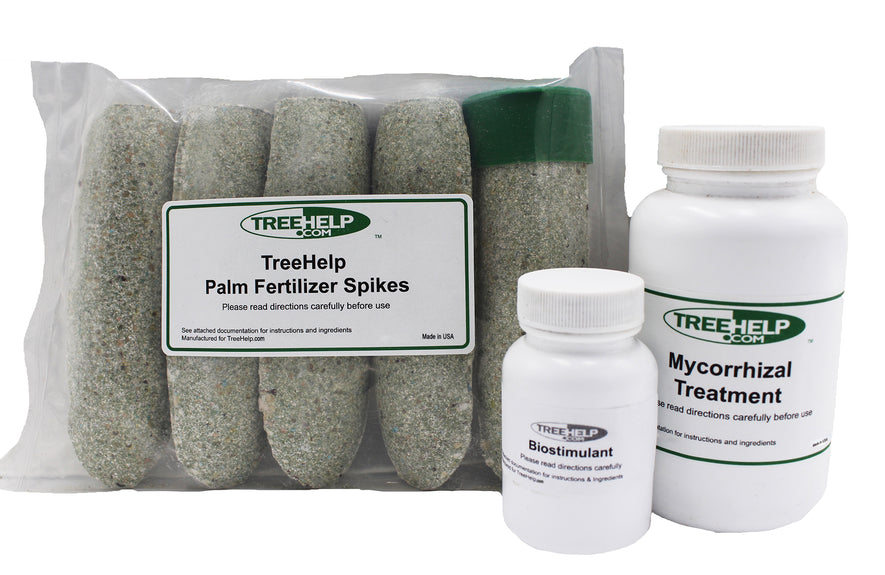
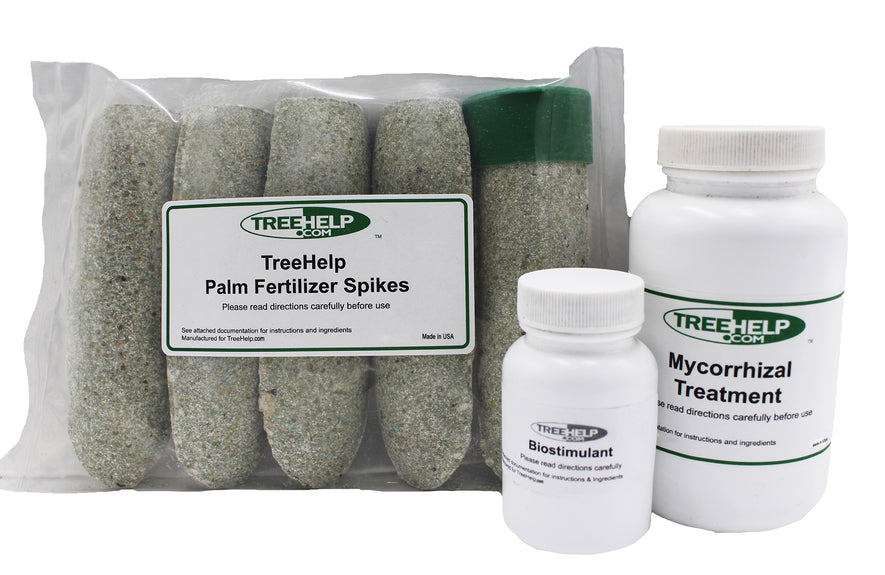
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Palms &... A complete do-it-yourself care package to maintain healthy and beautiful palms, palmettos and sagos. This kit is designed to treat...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Ash TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant ash trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits for...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
Captain Jack's Deadbug Dust, 1.5LB Captain Jacks tremendously popular family of Dead Bug Brew Spinosad products gets only better with this exclusive, ready-to-use dust formulation....
- Regular price
- $9.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $9.95
- Unit price
- per
-
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Redwood TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant Redwood trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits for...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Arborvitae TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant Arborvitae trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits for...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
-
Malathion 50E Insect Control 16oz. Concentrate Use on fruits, vegetables and ornamentals. One pint makes 50 gallons of spray, re-apply every 7 to 10 days for...
- Regular price
- $19.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $19.95
- Unit price
- per
-
TreeHelp Annual Care Kit: Olive TreeHelp developed easy-to-use Annual Care Kits to help homeowners maintain healthy and vibrant Olive trees. TreeHelp Annual Care Kits for...
- Regular price
- $33.95
- Regular price
-
- Sale price
- $33.95
- Unit price
- per
National Arbor Day Sale: free shipping on most orders over $69.95*